Hemoglobin
October 6, 2011 in Protein
On Monday, February 4th, 2008, the students in Mrs Shuster’s third grade class at École F.A.C.E. School were magnetized by the presentation by university students Sabrina Beiba (BFA Art Education, Concordia U.) and Caroline Proulx (M.Sc., U. Montréal) as they learned about the importance of iron in hemoglobin the “Protein of Life” in our second Molecules of Life Project (MLP) in Montreal.
Sabrina and Caroline led a discussion that covered nutrition, the circulatory system and the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide by iron in red blood cells.

After refreshing the students on laboratory safety, Caroline helped a student volunteer perform the ferric chloride test in which a brown suspension of iron chloride in water was added to a suspension containing an amino acid (the building blocks of proteins) producing a bright yellow solution, which drew everyone’s attention.
Packaging materials from various foods were distributed and the students were asked to read the Nutrition Facts and to determine which foods contained the most iron. Sabrina showed the students pictures of different foods and reminded the students that foods like raisins and spinach were good sources of iron.
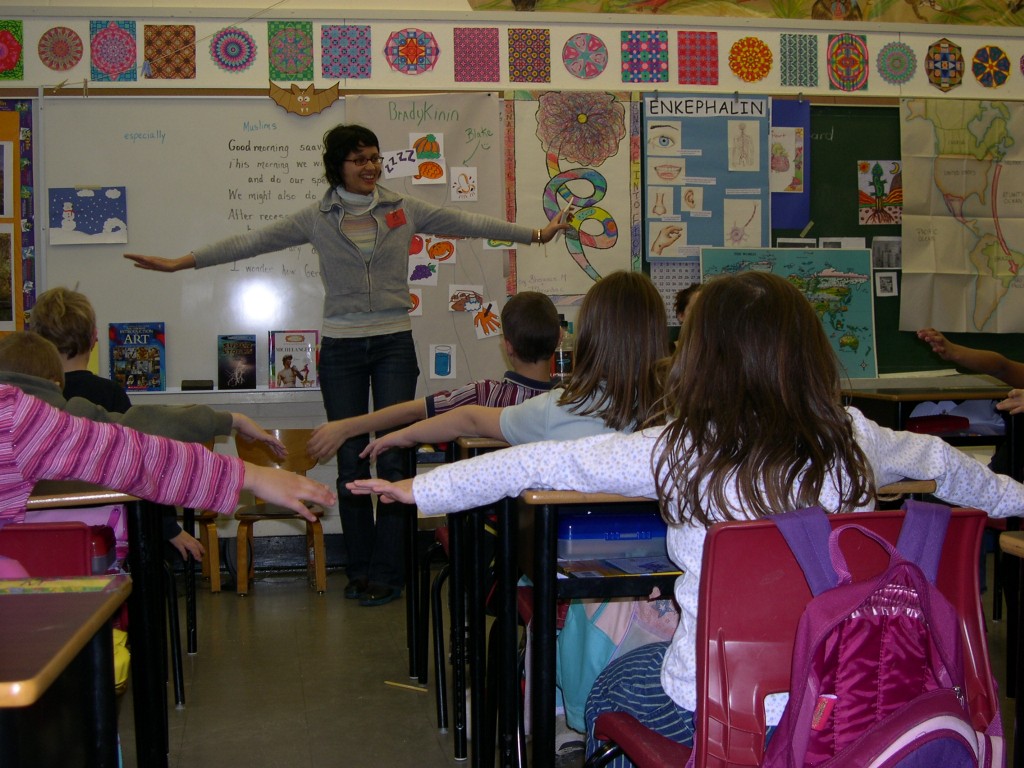
Sabrina and Caroline then led the students through the circulatory system. The students were first asked to each make a fist in order to perceive the size of their hearts, which pump blood throughout the body. Like tiny school buses which pick kids up and drive them to school and back, red blood cells were described as transportation machines which use iron contained in the protein hemoglobin to carry oxygen from the lungs to the cells and carbon dioxide from the cells back to the lungs. Like a fire requires oxygen to burn wood producing carbon dioxide, light and heat, the cells use oxygen to burn carbohydrates and sugars making carbon dioxide and energy.
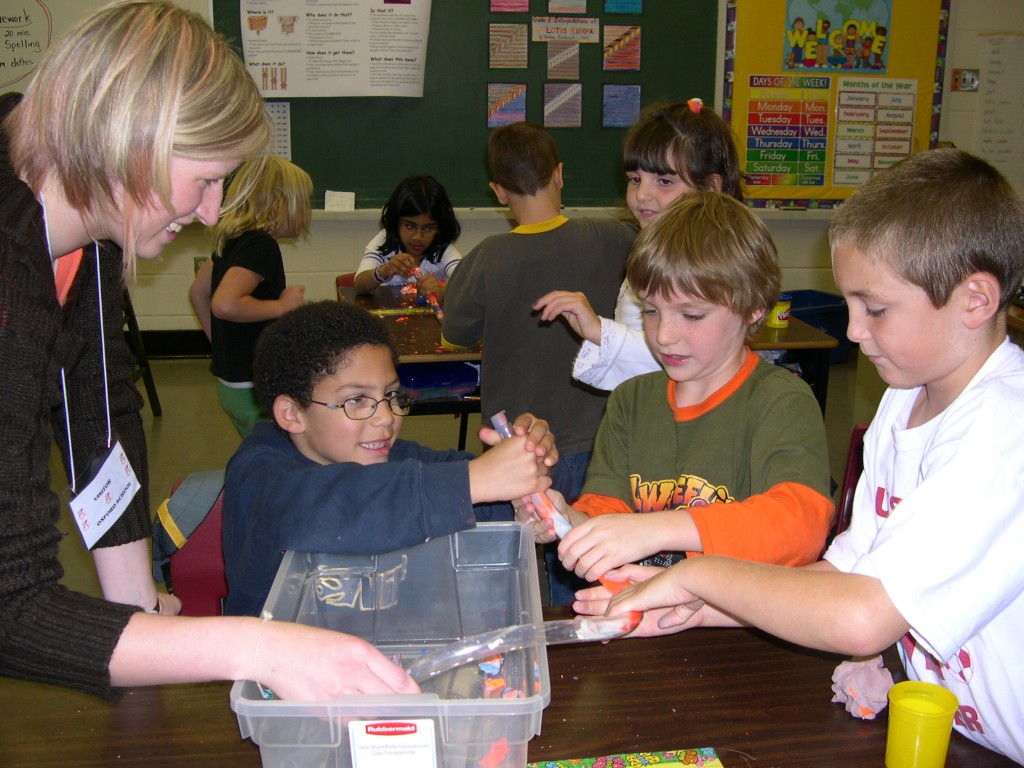
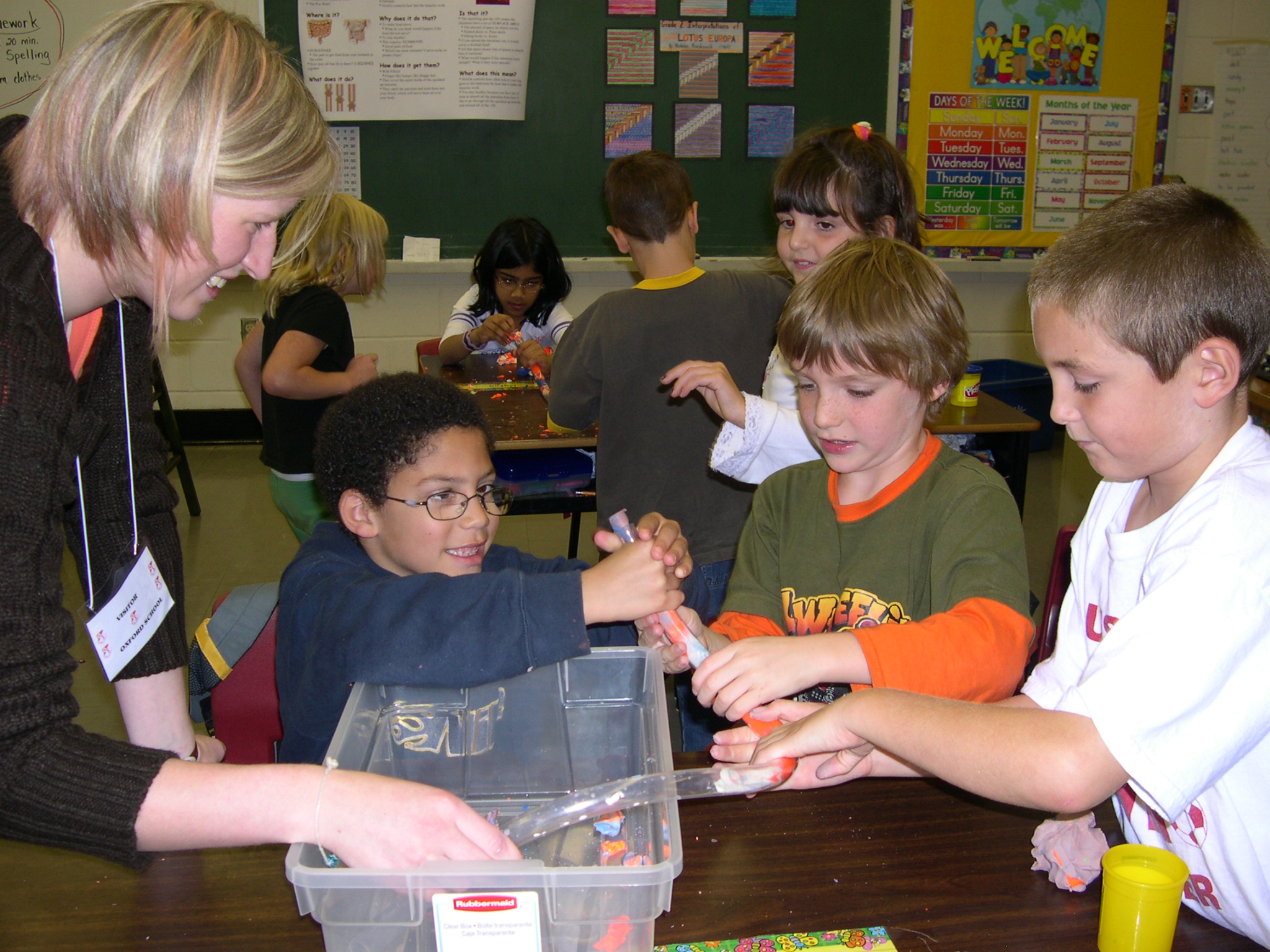
Studying iron as an element which can grab onto gasses like oxygen and carbon dioxide as well as building blocks like amino acids, the students were instructed on how to use iron as a pigment for dyeing fabric. Employing clips and other metal objects made from iron, the students used rust (iron oxide) to bind to cotton as they worked in teams to prepare four banners.
They pleated the fabric. Clipped the pleats together using metal clips. In some cases, they wrapped iron objects with the fabric which was secured with clips.
Finally, they soaked the bound-up cotton fabrics in water. In one case, they added a little vinegar to see what might happen as well. The next day, they removed the clips and saw that the rust had dyed their banners an orange-brown color.
With some extra time, Caroline and Sabrina described how a modification of one amino acid in the protein hemoglobin can cause blood cells to change their shapes from disc-like cells into sickle shaped cells in the disease sickle cell anemia. By passing down a tube round chips to represent normal red blood cells and shell-shaped macaroni to represent sickle cells, they demonstrated how the sickle-shaped macaroni could block the flow through the tube, in the way that sickle cells may inhibit blood flow in sickle cell anemia, and explained that this could cause less oxygen to flow to the cells, which results in less energy.
WIth five more proteins scheduled this year, we thanked team hemoglobin for an iron-clad MLP performance at FACE.
For more information see:
Ferric Chloride Test: www.wellesley.edu/Chemistry/chem211lab/Orgo_Lab_Manual/Appendix/ClassificationTests/phenol_amine_nitro.html
The circulatory system: www.globalclassroom.org/hemo.html
Rust Dyeing: www.prairiefibers.com/Rust%20Dyeing.htm
Sickle Cell Anemia: www.kidshealth.com/teen/diseases_conditions/blood/sickle_cell_anemia.html